Modern Medicine: Intervention & Control Model
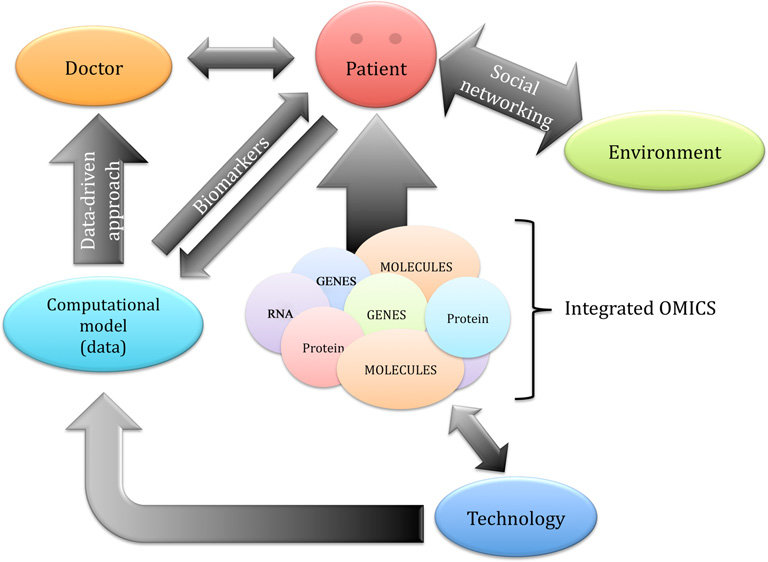
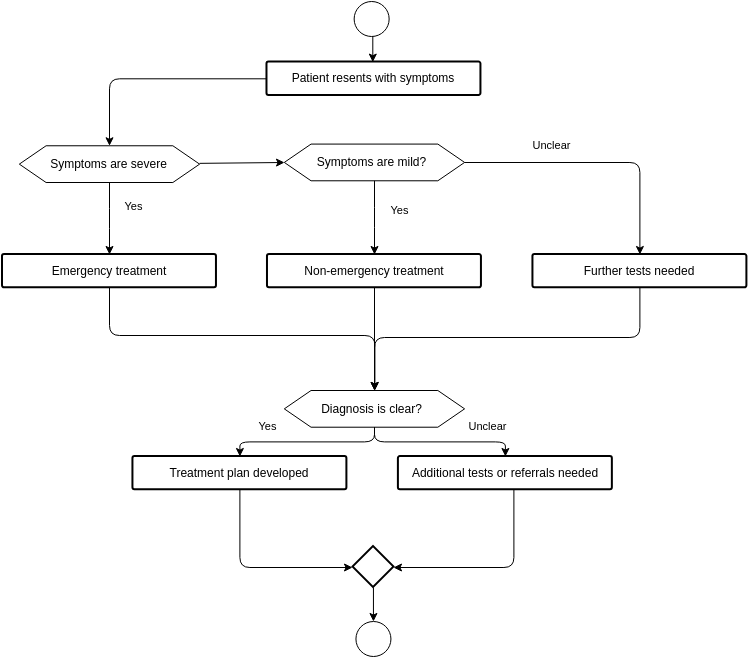
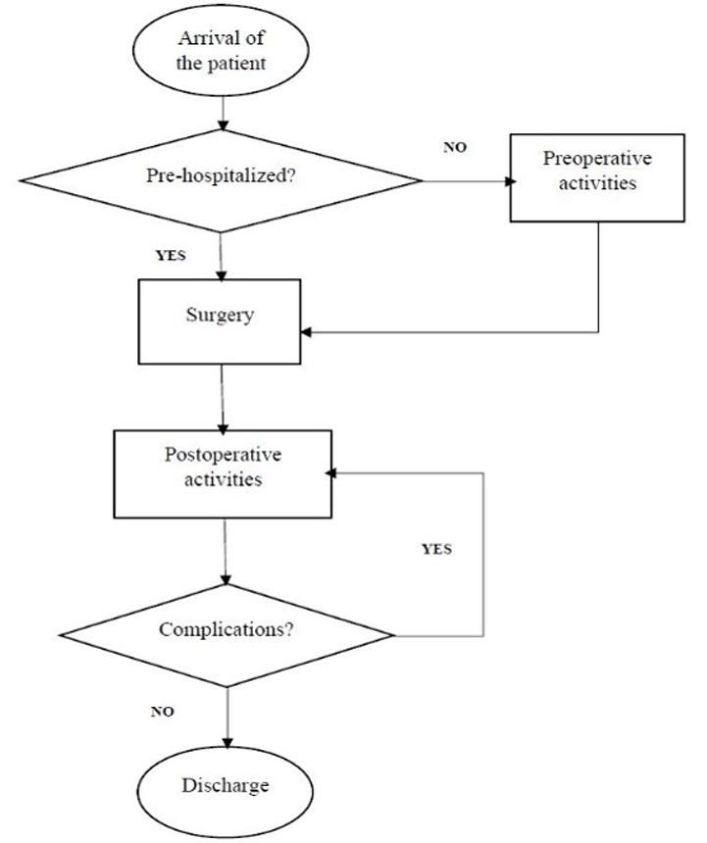
Visual concept
A linear, clinical flow:
Symptom → Diagnosis → Intervention → Stabilization
Explanation (terminology-accurate)
Modern medicine operates primarily within an interventional paradigm. The clinical workflow is optimized to:
This model excels in acute pathology, where speed, precision, and control are lifesaving. The system is intentionally designed for risk containment, not long-term biological reorganization.
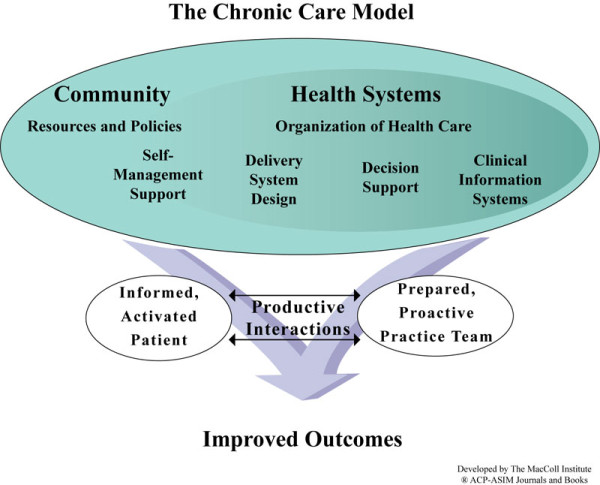
Acute Success vs. Chronic Limitations
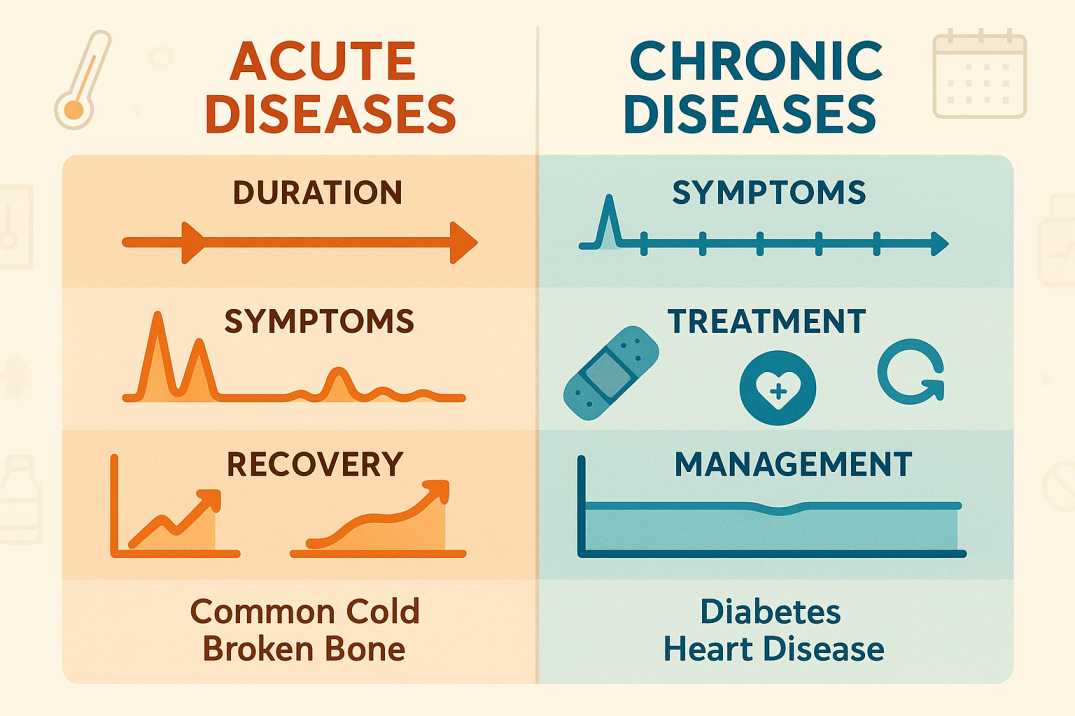

Visual concept
Split image:
Explanation
In acute conditions, intervention interrupts disease processes effectively.
In chronic or complex conditions, the same model often:
manages surface expressions of dysfunction
stabilizes biomarkers
delays progression
Without necessarily restoring:
homeostatic regulation
immune-metabolic coherence
tissue-level regeneration
This creates a maintenance loop, not biological resolution.
Symptom Management vs. Biological Healing

Visual concept
Two layers:
Explanation
Symptom control alters outputs.
Biological healing restores the internal environment that produces those outputs.
Healing requires:
Suppression alone does not equal regeneration.
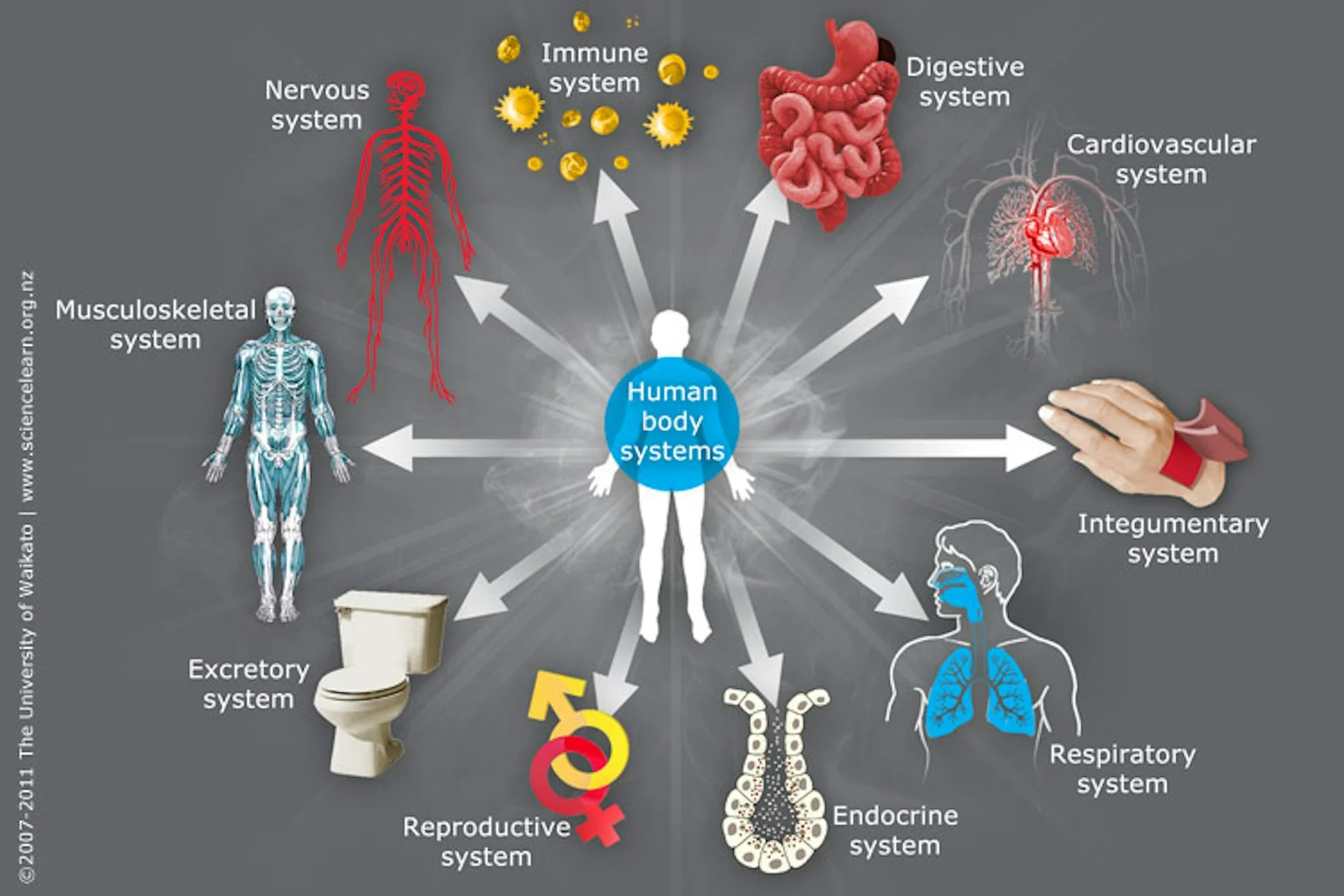
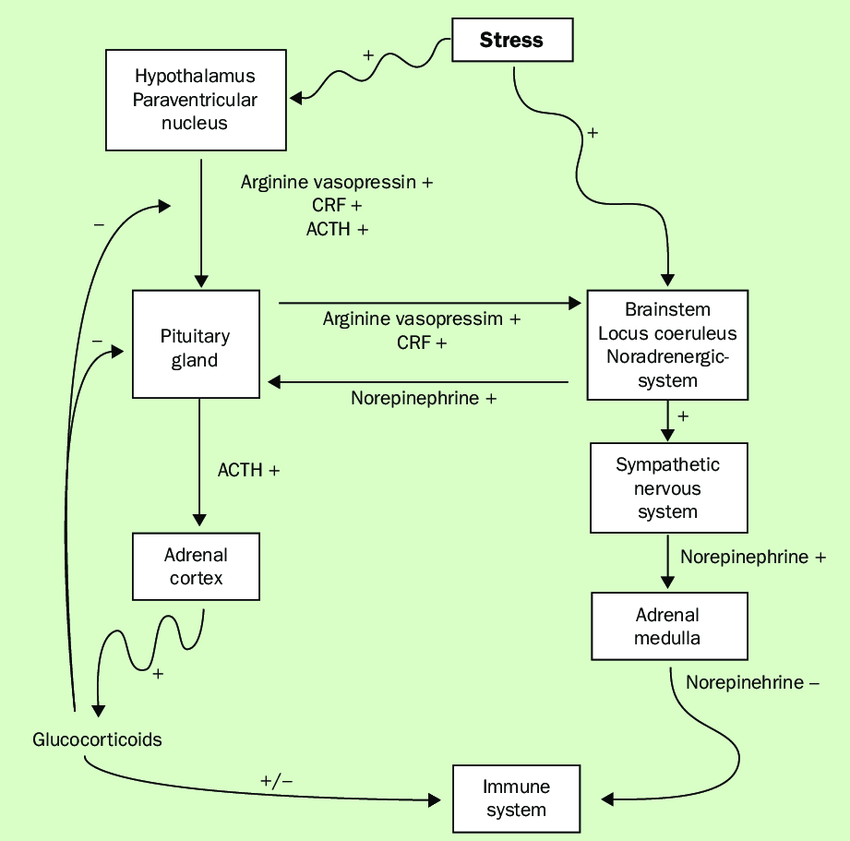
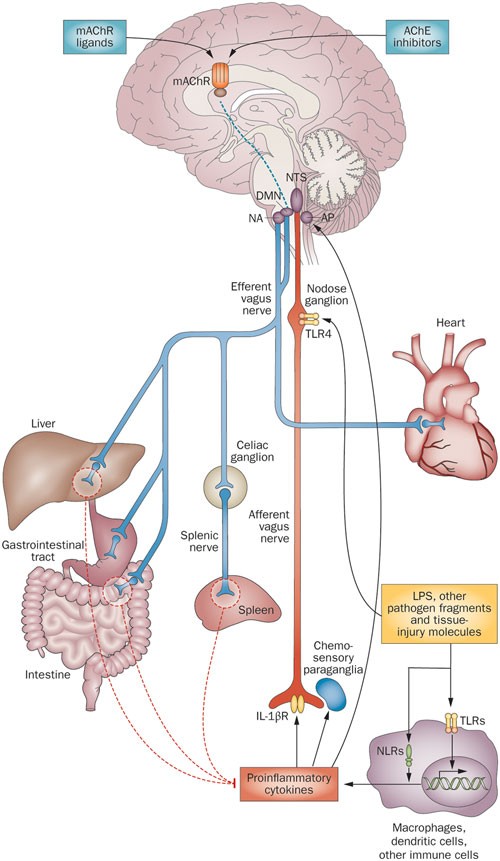
The Body as an Integrated Biological Network
>
Visual concept
Network diagram showing:
Explanation
Systems biology demonstrates that physiological function emerges from network interactions, not isolated organs or pathways.
Intervening in one node without addressing system-wide regulation often leads to:
Long-term coherence requires system-level support, not isolated correction.
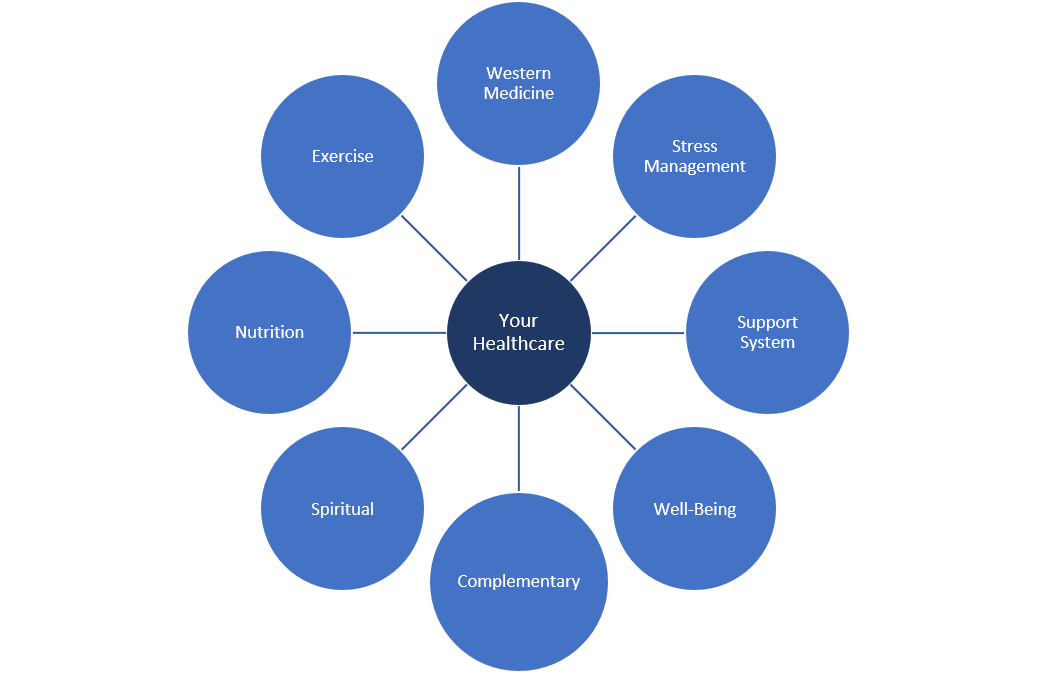
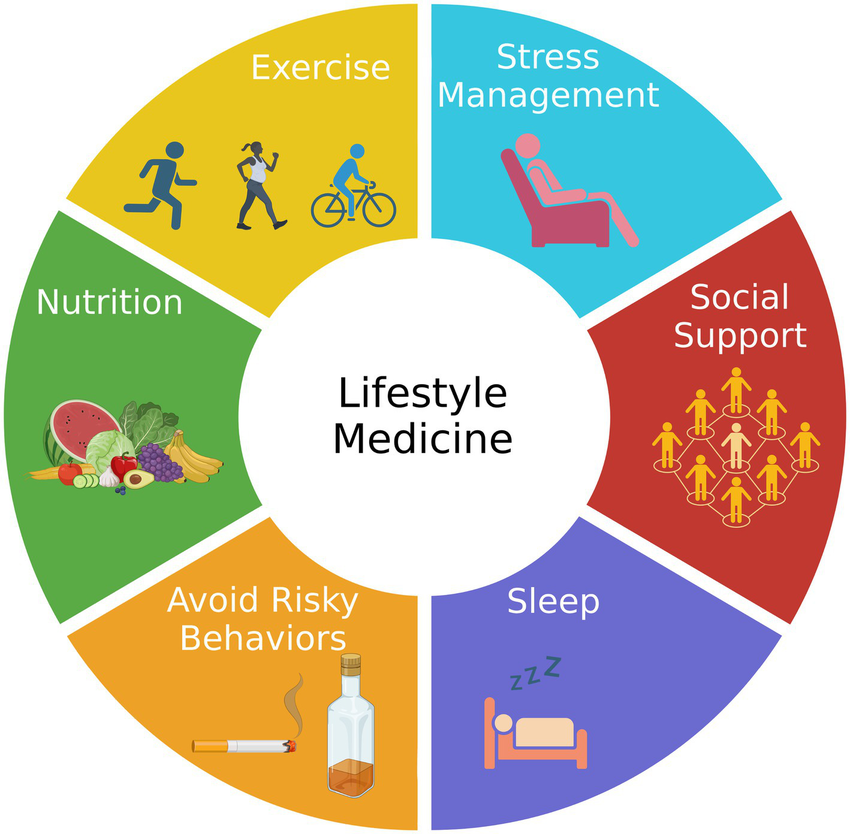
From Intervention to Cooperation With Biology
Visual concept
Shift from forceful intervention to supportive environment:
Explanation
Emerging complementary approaches aim to:
support regulatory systems
enhance biological resilience
create conditions for self-organization and repair
This is not anti-medicine.
It is medicine extended beyond crisis response.
Closing Synthesis (Visual Caption Text)
Control stabilizes.
Cooperation restores.
Modern medicine remains essential and irreplaceable.
But when the body is treated as a living system, healing becomes a process of alignment—not suppression.
Blog MiraBiotic®

Short, evidence-informed reads for everyday wellness. Explore topics across immunity, microbiome, metabolic balance, and neuro health.
Recent Blogs
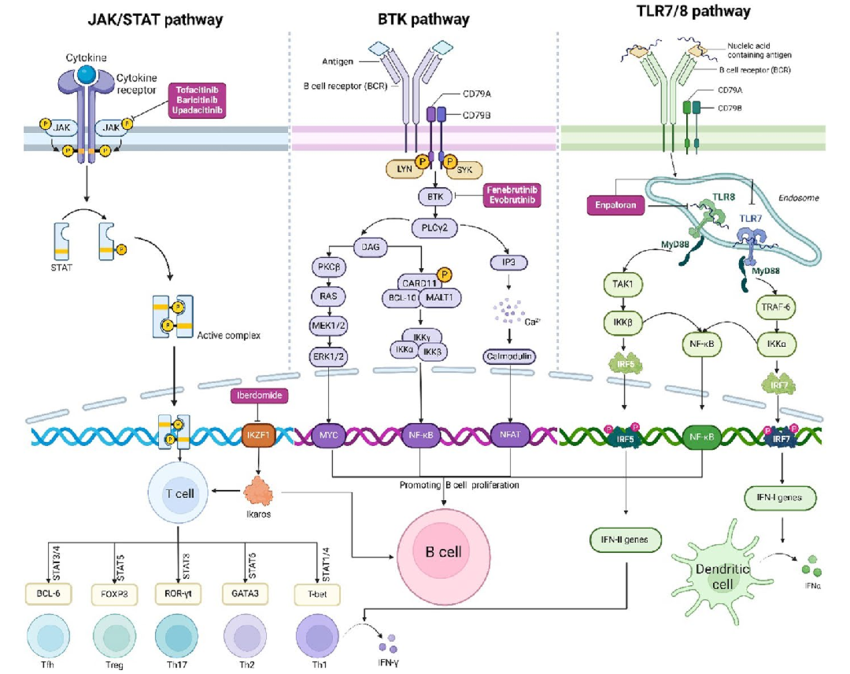
What Does Biological Reset Mean – and Why Does the Body Need It?
Jan 12, 2026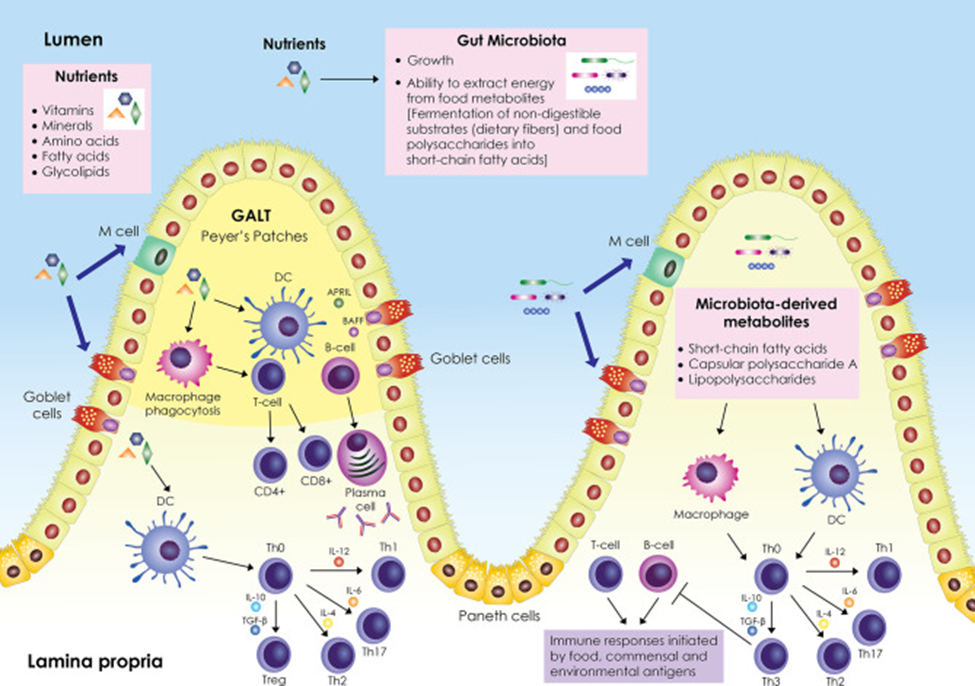
A Systems-Based Model of Biological Support with MiraBiotic
Jan 06, 2026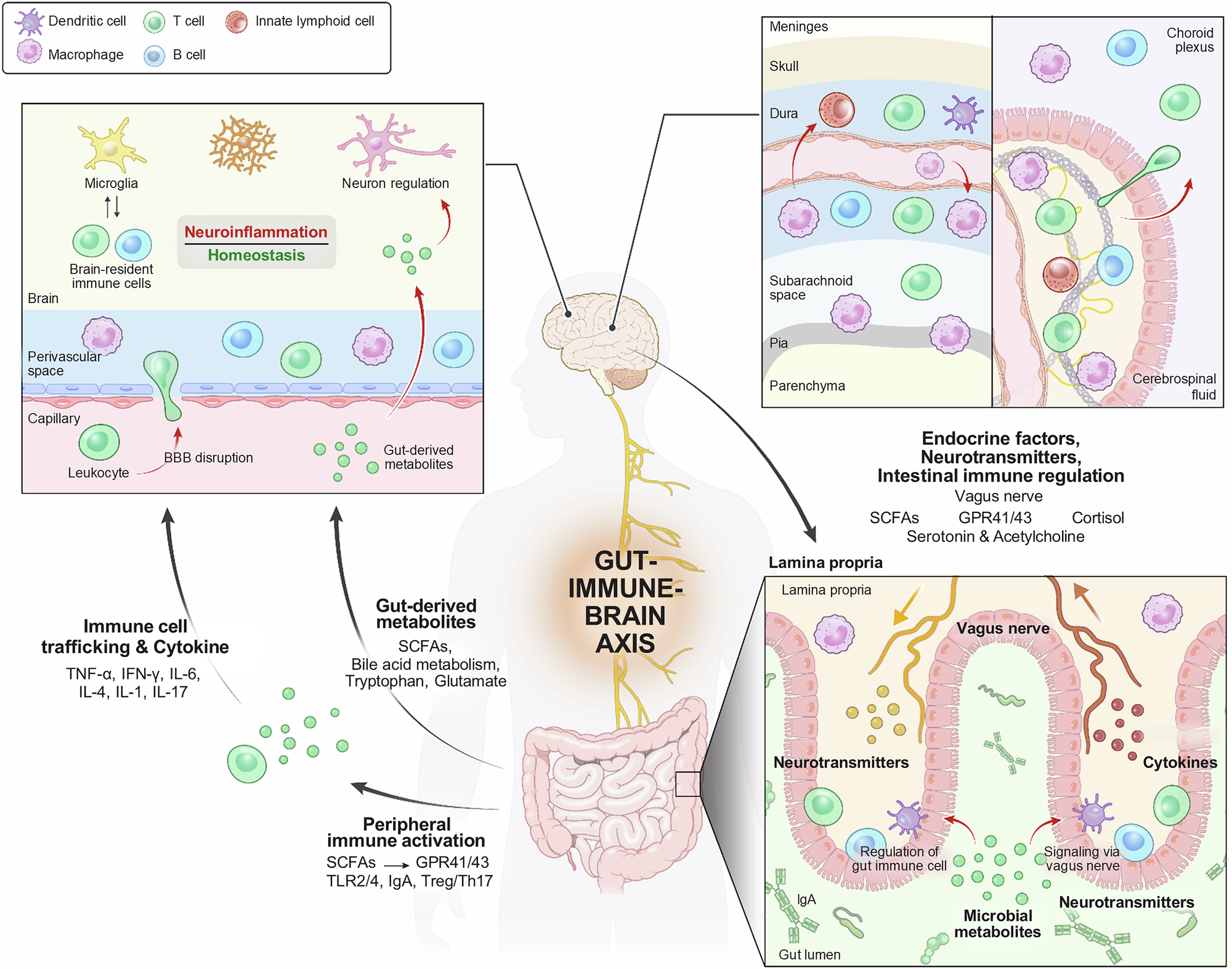
Inflammation as a Systemic Signal — Not a Disease
Jan 20, 2026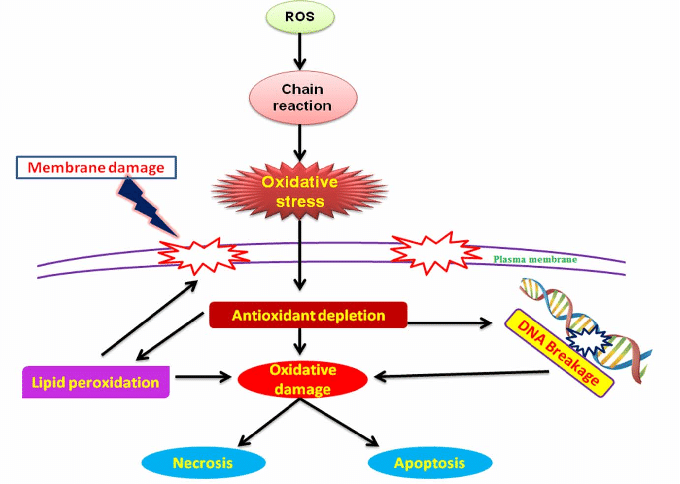
The Body’s Biological Intelligence – More Advanced Than We Think
Jan 19, 2026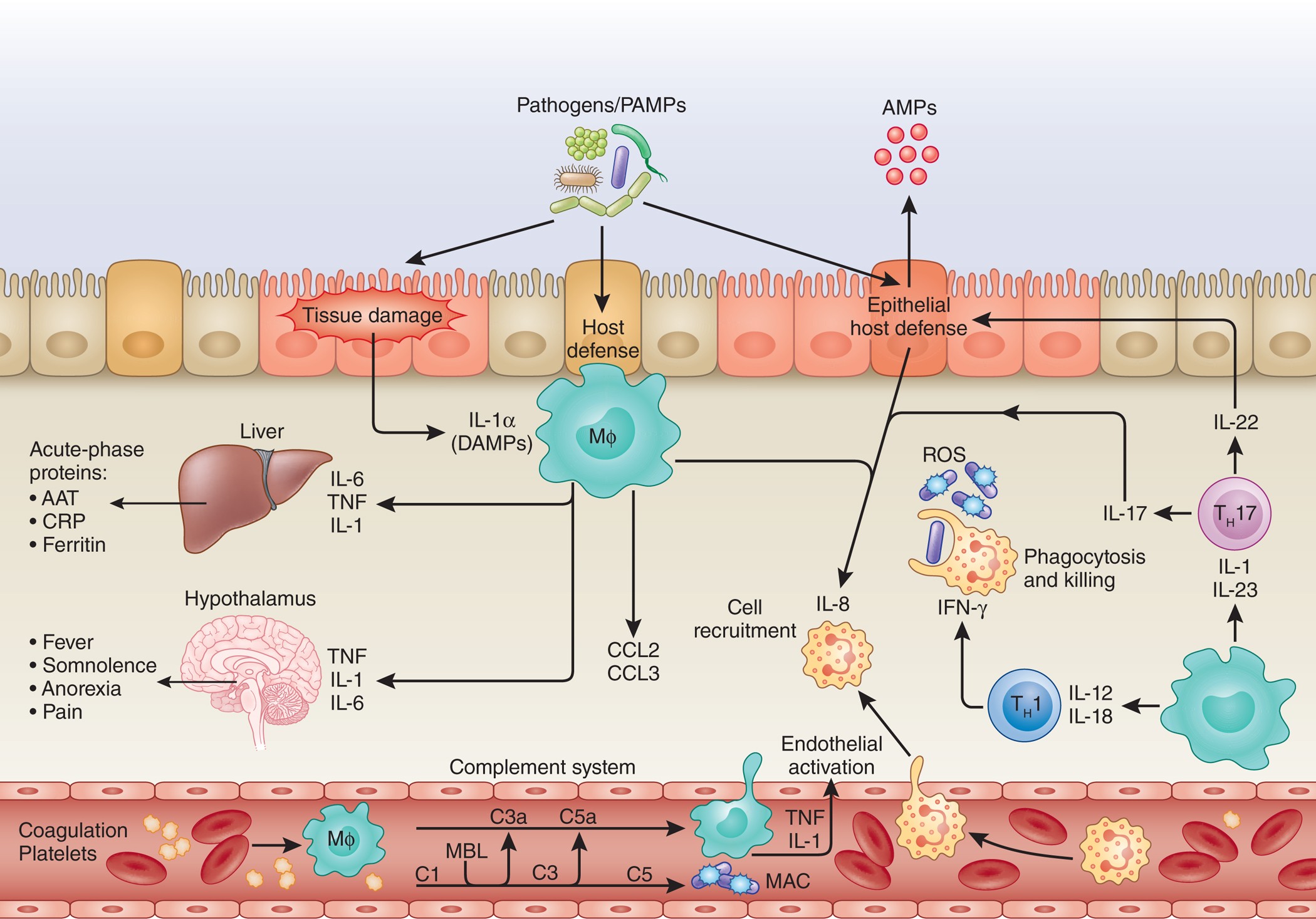
Why Chronic Diseases Are Rarely “Cured” in Current Medical Models
Jan 26, 2026Newsletter
Get new posts in your inbox.
